In today’s rapidly evolving application landscape, containerization and container orchestration have become essential technologies for enabling agility, scalability, and portability. Azure provides comprehensive support for containerization and offers a fully managed Kubernetes service, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), enabling developers and IT professionals to deploy and manage containerized applications at scale.
Understanding Containerization:
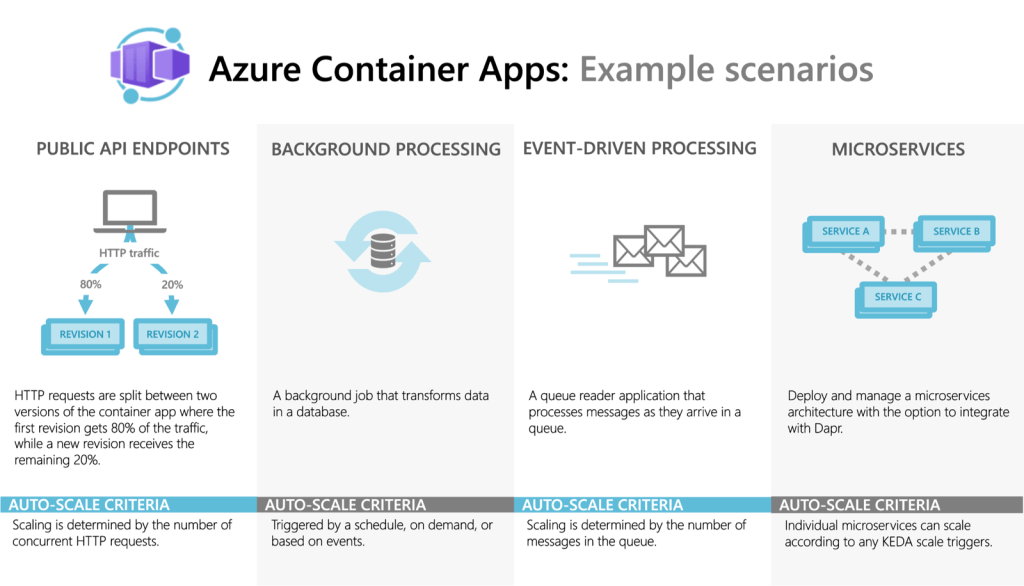
*image sourced from Google
Containerization is a virtualization approach that packages applications and their dependencies into isolated, lightweight, and portable containers. Containers share the host operating system kernel, enabling efficient resource utilization and consistent application behavior across different environments. Key benefits of containerization include:
1. Portability: Containers encapsulate the entire application runtime environment, ensuring consistent behavior across different hosting platforms and environments.
2. Isolation: Each container runs in an isolated environment, preventing conflicts with other containers or the host system, and ensuring secure and reliable application execution.
3. Efficiency: Containers share the host operating system kernel, resulting in more efficient resource utilization compared to traditional virtual machines.
4. Scalability: Containers can be easily scaled horizontally by spinning up additional instances, enabling applications to handle fluctuating demand and traffic loads.
Azure Container Registry (ACR):
Azure Container Registry is a private, centralized registry for storing and managing container images. Key features of ACR include:
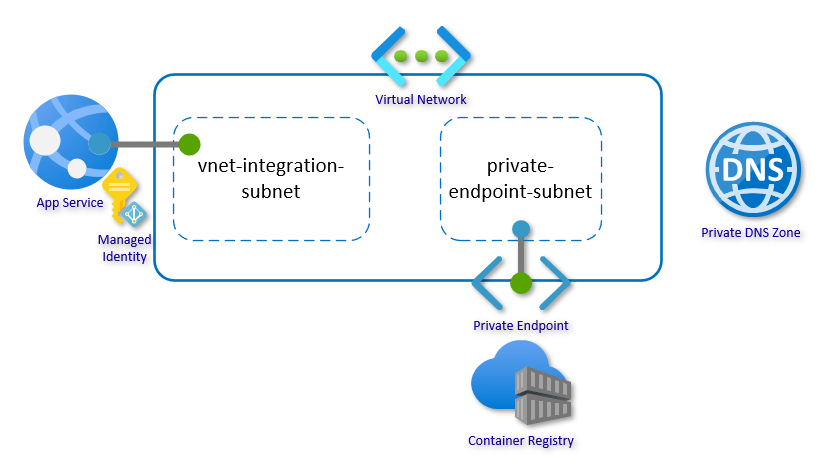
*image sourced from Google
1. Secure Image Storage: Store and manage Docker container images in a secure, private registry hosted in Azure.
2. Geo-Replication: Replicate container images across multiple Azure regions, ensuring high availability and low-latency access to images.
3. Vulnerability Scanning: Automatically scan container images for known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, enabling proactive security measures.
4. Integrated CI/CD: Integrate ACR with Azure DevOps Services or other CI/CD pipelines for automated image building, testing, and deployment.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS):

*image sourced from Google
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a fully managed Kubernetes service that enables you to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications efficiently. Key features of AKS include:
1. Simplified Provisioning: Rapidly provision Kubernetes clusters with automated configuration, updates, and scaling, reducing the operational overhead of managing Kubernetes.
2. Integrated Networking: Leverage Azure Virtual Networks and networking services to securely connect and manage communications between your AKS clusters and other Azure resources.
3. Advanced Scheduling: Utilize advanced scheduling capabilities, such as node pools, pod disruption budgets, and node auto-scaling, to optimize resource utilization and ensure high availability.
4. Monitoring and Logging: Integrate with Azure Monitor for comprehensive monitoring and logging of your AKS clusters, enabling proactive issue detection and troubleshooting.
5. Secure Deployments: Leverage Azure Active Directory for authentication and role-based access control (RBAC) to secure your AKS deployments and restrict access to authorized users and services.
Deploying Containerized Applications on Azure:
Azure provides various options for deploying and managing containerized applications, including Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Azure Container Instances (ACI), and Azure Web Apps for Containers. Here’s an overview of these services:
1. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): AKS is the recommended option for deploying and managing production-grade containerized applications at scale. It provides a fully managed Kubernetes environment, enabling you to leverage the power of Kubernetes for orchestrating and managing your containerized workloads.
2. Azure Container Instances (ACI): ACI is a serverless container offering that allows you to run containerized applications without provisioning and managing virtual machines or clusters. ACI is suitable for burst workloads, batch processing, and lightweight containerized applications that don’t require the full capabilities of Kubernetes.
3. Azure Web Apps for Containers: This service allows you to deploy and run containerized web applications on a fully managed platform as a service (PaaS) offering. It simplifies the deployment and scaling of containerized web apps while providing features like continuous deployment, custom domains, and SSL/TLS support.
Best Practices for Containerization and Kubernetes in Azure:
To effectively leverage containerization and Kubernetes in Azure, it’s essential to follow best practices and adopt a DevOps mindset:
1. Embrace DevOps and CI/CD: Implement DevOps practices and continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to automate the build, testing, and deployment of containerized applications, ensuring consistency and reliability.
2. Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Define and manage your container infrastructure as code using tools like Azure Resource Manager templates or Terraform, enabling version control, repeatable deployments, and consistent environments.
3. Utilize Managed Services: Leverage fully managed services like Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and Azure Container Registry (ACR) to reduce operational overhead and benefit from automated updates, scaling, and security features.
4. Monitor and Observe: Implement comprehensive monitoring and observability practices for your containerized applications and Kubernetes clusters, leveraging tools like Azure Monitor, Prometheus, and Grafana to gain insights into application performance, resource utilization, and potential issues.
5. Secure Container Deployments: Implement security best practices, such as using private container registries, network isolation, RBAC, and vulnerability scanning, to protect your containerized applications and Kubernetes clusters from potential threats.
6. Optimize Resource Utilization: Leverage advanced scheduling capabilities in Kubernetes, such as node pools, auto-scaling, and resource quotas, to optimize resource utilization and ensure efficient and cost-effective container deployments.
7. Plan for Scalability and High Availability: Design your containerized applications and Kubernetes clusters with scalability and high availability in mind, utilizing features like load balancing, replication, and geo-replication to handle fluctuating demand and ensure application uptime.
By embracing containerization and Kubernetes in Azure, developers and organizations can unlock the benefits of agility, scalability, and portability, enabling them to build and deploy modern, cloud-native applications more efficiently and effectively.
