*image sourced from Google
In today’s digital landscape, delivering web applications efficiently and seamlessly is crucial for meeting user expectations and staying ahead of the competition. Azure Web Apps, a fully managed platform as a service (PaaS) offering from Microsoft, empowers developers to build, deploy, and manage web applications with ease, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Deploying Web Apps on Azure:
Azure Web Apps supports various deployment options, catering to different development workflows and preferences. Here are some common deployment methods:
1. Azure App Service Deployment Center: This built-in deployment feature within the Azure portal allows you to connect your web app to a source control repository (e.g., GitHub, Azure Repos, BitBucket) and enable continuous deployment. With each commit to your repository, the deployment center automatically builds and deploys your application to Azure. The integration with popular source control systems makes it easy to manage your code, track changes, and collaborate with your team.
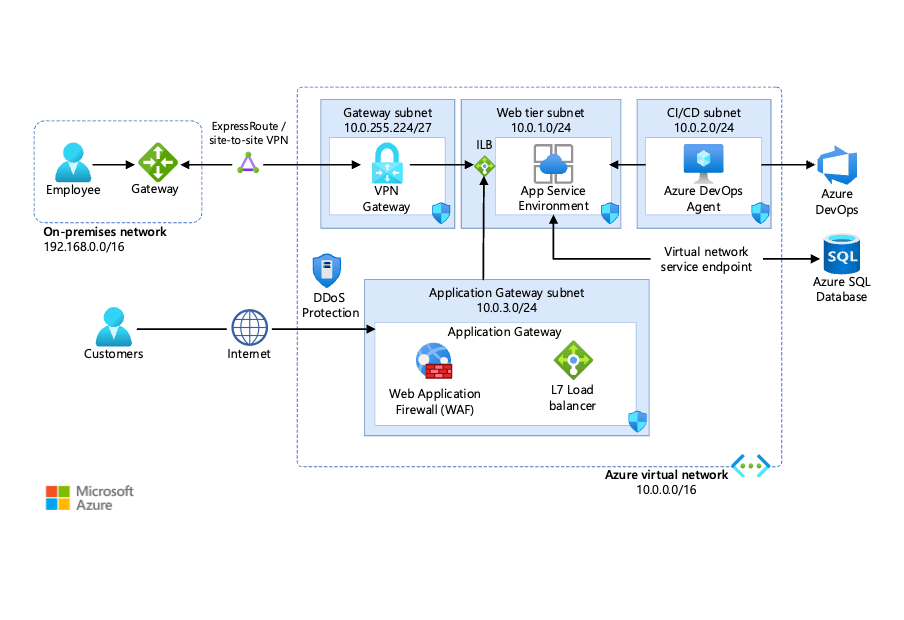
2. Azure DevOps: Integrate your web app deployment with Azure DevOps, Microsoft’s suite of services for version control, agile planning, and continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD). Configure build and release pipelines to automate the entire deployment process, from compiling code to deploying to multiple environments (e.g., development, staging, production). Azure DevOps also offers features like work item tracking, test management, and reporting, making it an ideal choice for teams looking for a comprehensive development management solution.
3. FTP/FTPS: For simpler deployments or legacy applications, you can use FTP or FTPS to upload your application files directly to the web app’s file system. This method is suitable for small-scale applications or when you need to quickly deploy a static website. However, it lacks the automation and collaboration benefits offered by other deployment methods.
4. Cloud Shell: Azure Cloud Shell is a browser-based command-line experience that allows you to manage Azure resources, including deploying web apps, directly from the Azure portal or a remote machine. With support for Bash and PowerShell, you can use familiar command-line tools and scripts to automate and manage your deployments.
5. Local Git Deployment: Developers can also deploy their applications using Git directly from their local development environment, enabling a more streamlined and familiar workflow. This approach allows you to leverage Git’s version control capabilities while deploying your application to Azure with minimal configuration.
Managing and Scaling Web Apps:
Once deployed, Azure Web Apps provides a range of features and capabilities for managing and scaling your applications effectively:
1. Auto-scaling: Configure auto-scaling rules to automatically adjust the number of instances (scale out) or allocated resources (scale up) based on predefined metrics like CPU utilization or HTTP queue length. This ensures optimal performance and cost efficiency by matching resource allocation to real-time demand. Auto-scaling can be configured based on a schedule or specific performance thresholds, allowing you to fine-tune your application’s scalability to meet your unique requirements.
2. Deployment Slots: Create and manage multiple deployment slots for each web app, enabling techniques like blue-green deployments, canary releases, and A/B testing without impacting the production environment. Deployment slots allow you to test new features, validate performance, and ensure compatibility before swapping the staging environment with the production environment. This approach minimizes downtime and reduces the risk of deploying untested or unstable code to your live application.
3. Backup and Restore: Automatically back up your web app’s content, configuration, and databases at scheduled intervals or on-demand. Restore these backups to a different web app or to the same web app at a previous point in time, ensuring data protection and disaster recovery. Azure Web Apps also supports geo-redundant backups, enabling you to store your backups in different regions for added resilience and faster recovery in case of a regional outage.
4. Monitoring and Diagnostics: Monitor your web app’s performance, diagnose issues, and gain insights into application health and resource utilization using Azure Application Insights, Log Analytics, and other monitoring tools. These tools provide real-time telemetry, customizable dashboards, and powerful analytics capabilities to help you identify and resolve performance bottlenecks, errors, and other issues impacting your application’s user experience.
5. Security and Compliance: Secure your web apps with built-in features like SSL/TLS encryption, authentication and authorization options (e.g., Azure Active Directory, social providers), and compliance certifications (e.g., ISO, PCI DSS, HIPAA). Azure Web Apps also supports virtual network integration, allowing you to isolate your web app within your own virtual network for enhanced security and network control.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the deployment and management capabilities of Azure Web Apps, highlighting its versatility, scalability, and ease of use. In the following articles, we’ll dive deeper into specific features and best practices for building and deploying high-performance, secure, and scalable web applications on Azure. By leveraging Azure Web Apps, developers can streamline their development workflows, automate deployment processes, and focus on delivering innovative and engaging web applications to their users.
