*image sourced from Google
Azure offers a vast array of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of developers. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most popular and powerful services that can significantly enhance your development experience and application capabilities.
Azure App Service: A Fully Managed Platform for Web Applications and APIs
Azure App Service is a fully managed platform that allows you to quickly build, deploy, and scale web applications and APIs written in various languages, including .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and more. App Service supports multiple deployment options, such as Git, Docker containers, and continuous deployment from Azure DevOps, providing flexibility and ease of use.
Azure Functions: Embrace Serverless Computing
Azure Functions enables you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. Functions are event-driven, scalable, and charged based on consumption, making them ideal for building microservices, data processing pipelines, and integrating with other Azure services. With Azure Functions, you can focus on writing code and let Azure handle the infrastructure.
Azure Cosmos DB: A Globally Distributed, Multi-Model Database Service
Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed, multi-model database service that supports various data models, including key-value, document, graph, and columnar. Cosmos DB offers features like multi-master replication, automatic indexing, and tunable consistency levels, ensuring high availability, scalability, and low latency for your applications.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Managed Kubernetes for Containerized Applications
Deploy and manage containerized applications at scale with AKS, a fully managed Kubernetes service. AKS simplifies the provisioning, scaling, and management of Kubernetes clusters, enabling rapid deployment and scaling of containerized workloads. With AKS, you can easily orchestrate your containerized applications, ensuring efficient resource utilization and high availability.
Azure Cognitive Services: Infuse Your Applications with Intelligent Capabilities

*image sourced from Google
Azure Cognitive Services offers pre-built AI models and APIs that enable you to infuse your applications with intelligent capabilities. Cognitive Services includes functionalities like computer vision, speech recognition, language understanding, and decision-making, empowering you to create intelligent and engaging user experiences.
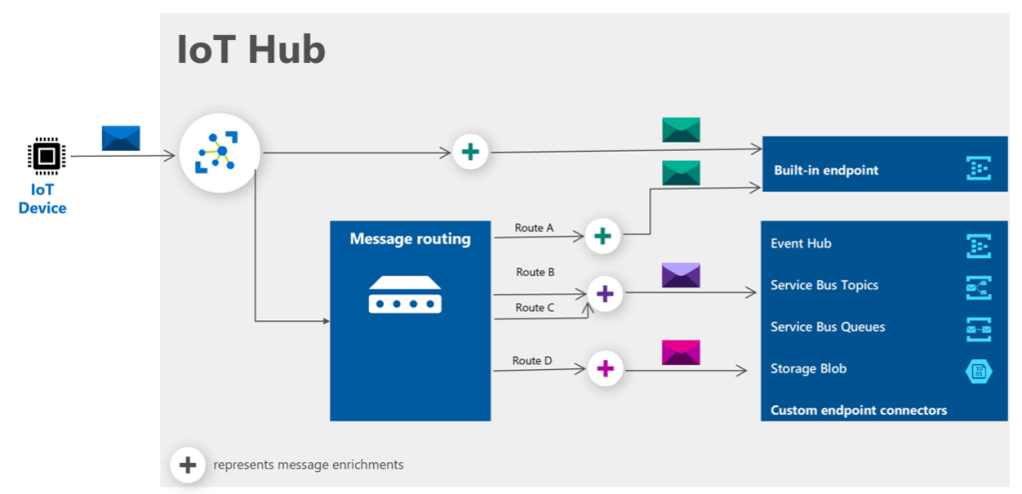
Azure IoT Hub: Build and Manage Secure, Scalable IoT Solutions
*image sourced from Google
Azure IoT Hub enables you to connect, monitor, and manage billions of IoT devices with ease. Leverage cloud-to-device messaging, device twin management, and seamless integration with other Azure services for comprehensive IoT application development. With Azure IoT Hub, you can create secure, scalable, and reliable IoT solutions.
Azure DevOps: Streamline Your Development Lifecycle

*image sourced from Google
Azure DevOps is a suite of services for version control, agile planning, continuous integration and deployment, automated testing, and monitoring. DevOps enables collaborative development, automated release pipelines, and seamless integration with other Azure services, ensuring a smooth and efficient development lifecycle.
Azure Machine Learning: Build, Train, and Deploy Machine Learning Models at Scale

*image sourced from Google
Azure Machine Learning is a comprehensive service that supports the entire machine learning lifecycle, from data preparation and model training to deployment and management. With Azure Machine Learning, you can build, train, and deploy machine learning models at scale, infusing your applications with intelligent capabilities.
These are just a few examples of the powerful services Azure offers for developers. Throughout the remaining articles in this series, we’ll dive deeper into specific services, exploring their features, use cases, and best practices for leveraging them in your development projects. By familiarizing yourself with these services, you’ll be well-equipped to build, deploy, and manage modern, scalable, and secure applications on Azure.
